NutriScience for everybody
The Eidos diet
The Eidos diet was created for people who care about their health and that want to prevent and reverse diseases mainly associated with nutritional behaviors. The Eidos diet emphasizes on a varied diet that besides satisfying all the daily nutritional requirements incorporates functional nutraceutical foods as the only way to guarantee a healthy lifestyle. This diet was created to help people. People who do not have a health care system can benefit greatly from this diet.
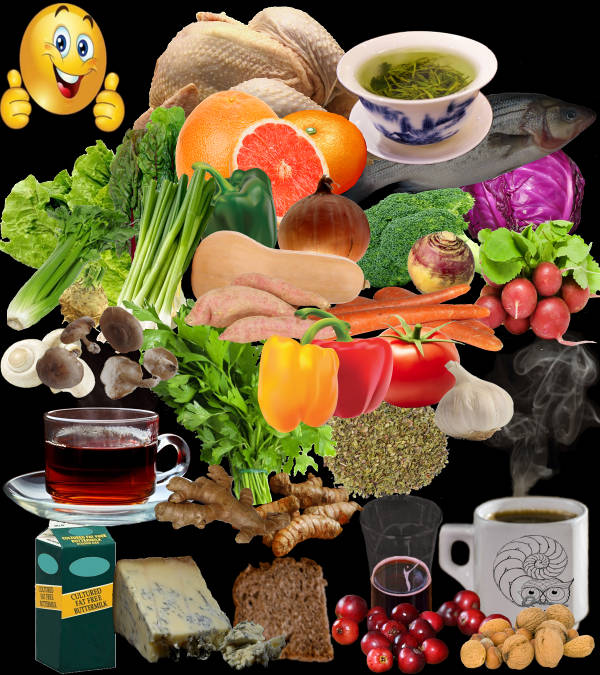

The Eidos diet is based on the Mediterranean diet and scientifically based eating patterns, as well as on the principle that food must confer benefits that promote health and prevent and reverse diseases.
The Eidos diet emphasizes on a varied diet. The diet must be composed of foods that in addition to satisfying all the daily nutritional requirements, also provide molecules with functional and nutraceutical properties that benefit the health with scientifically proven ability to prevent and reduce the risk of contracting diseases.
Today, the impact of diets on the health in different civilizations and cultures is well known. Modern diets are profoundly different from those consumed by our hunter-gatherer ancestors for millions of years prior to the Agricultural Revolution approximately 12.000 years ago; today, most of the food consumed worldwide is derived from domesticated plants and animals, as opposed to the wild varieties that made up the diet of preagricultural people, and an increased consumption of evolutionary novel foods and innovations related to food manufacturing, storage, and processing have dramatically changed the overall makeup and nutrient composition of human diets[2]. Also it is well know that in western countries, various illnesses and conditions, such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, gout, hypertension, coronary heart disease (CHD), and epithelial cell cancers, which are rare or virtually absent in hunter–gatherers, horticulturalists, and traditional pastoralists, are now increasing in younger age groups[3] in several part of the world with western diets.
The impact that different diet patterns, from different cultures, have on the health it is well known. Western diets, such as those based on fast foods, are responsible of the increase of obesity and some kind of diseases such as coronary and cardiovascular hearth diseases and diabetes type 2 while Mediterranean diets favor the health and longevity of people. These are two examples of how diets from different regions in the world can affect the health. Diseases of insulin resistance are frequently referred to as “diseases of civilization” and include: obesity, coronary heart disease (CHD), type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia such as elevated serum triacylglycerols, small-dense, LDL cholesterol and reduced HDL cholesterol; also it is likely that the metabolic syndrome may extend to other chronic illnesses and conditions that are widely prevalent in Western societies, including: myopia, acne, gout, polycystic ovary syndrome, epithelial cell cancers such as breast, colon, and prostate cancer, male vertex balding, skin tags and acanthosis nigricans; also it should be noted that the diseases of insulin resistance are rare or absent in hunter-gatherer and other less westernized societies living and eating in their traditional manner[5]. That foods might provide therapeutic benefits is clearly not a new concept. The tenet, “Let food be thy medicine and medicine be thy food” was embraced about 2500 years ago by Hippocrates, the father of medicine. However, this “food as medicine” philosophy fell into relative obscurity in the 19th century with the advent of modern drug therapy. In the 1900s, the important role of diet in disease prevention and health promotion came to the forefront once again[2].
Therefore, for those who wish to live a healthy lifestyle by choosing the Eidos diet, this diet should be a lifestyle choice and a personal conviction as the way to achieve strong adherence to the diet.
_______[1] Cseke, Leland J. Et al. 2006. Natural products from plants. Informa Taylor & Francis Group.
[2] Hasler, Clare M. 2002. Functional Foods: Benefits, Concerns and Challenges—A Position Paper from the American Council on Science and Health. J. Nutr. 132: 3772–3781.
[3] Bachelor’s thesis in Public Health Nutrition. 2012. The Evolution of the Human Diet. From Wild Meat, Fruits, and Tubers to Candy, Donuts, and Pizza.Oslo and Akershus University College.
[4] Carrera-Bastos, Pedro et al. 2011. The western diet and lifestyle and diseases of civilization. Research Reports in Clinical Cardiology: 2.
[5] Cordain , Loren et al. 2005. Origins and evolution of the Western diet: health implications for the 21st century. Am J Clin Nutr; 81:341–54.
Benefits of the Eidos diet

The Eidos diet is a diet that cares about the health and the nutritional status of people and was created for helping people. The Eidos diet includes food that have good quality nutritional properties that benefit the health. Diets with foods that satisfy all the daily nutritional requirement with functional and nutraceutical properties are the foundation for a good nutritional status and for having a healthy and a happy life promoting longevity.
The Eidos diet has wide beneficial effects on the health. This diet can help to prevent a wide range of diseases helping people with all kind of health condition. It is a good diet for lowering the cholesterol, treating obesity and weight loss without puting the health at risk. People with cancer can benefit from this diet because they can live with a better lifestyle and depending of the type and the stage of the cancer the disease could be reverted by eating specific kind of foods and in specific combinations and amounts. People with some kind of health condition that started the Eidos diet improved greatly their health condition.
Food processing, food conservation, daily eating with regular schedules, and healthy habits are part of the considerations that the Eidos diet takes an account.
The adherence to this diet can only be achieved by personal convictions because the Eidos diet needs to be a choice of a new lifestyle for those who wish to have a better health and a better quality of life.
Foods that you should avoid
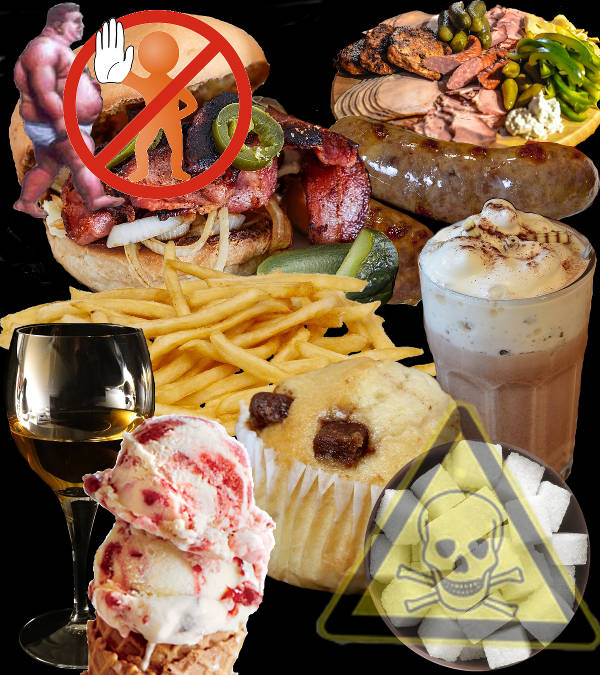

Foods high in fat, sugar, and salt should be avoided. They only should be eaten occasionally and in small amounts. Fast foods also are also called junk foods and they are foods with empty calories that mean foods with a lot of calories with poor nutritional value; where vitamins, minerals and/or fibers are absent or in very small quantities.
These foods are responsible of the nutritional diseases such as obesity, coronary heart disease, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia and other chronic diseases.
Diseases like coronary artery disease have seen a profound rise in developing an countries and such unhealthy junk food consumption is one of the notable factors to its contribution where healthy nutritious foods have been replaced by the new food mantra – JUNK FOOD!; in the context of world economy, junk food is a global phenomenon[1].
Sugar and food with added sugar should be avoided. The World Health Organization has recommended no more than 10% of calories from added sugars with an ultimate goal of reducing this to 5%.
___________
[1] Ashakiran and Deepthi, R. 2012. Fast Foods and their Impact on Health. JKIMSU, Vol. 1, No. 2.
Avoid or eat occasionally and in small quantities
Sugar. Foods with added sugar. Soda drinks. Alcoholic drinks. Fried foods. Ice cream. Pastry. Hamburgers. Sausage. Fatty foods. Candies. Salt. Canned foods. Smoked foods. Snak bars.
Healthy Eating: Eidos Pyramid
The Eidos diet is recommending the intake of foods servings and meals frequency as it is indicated in the following healthy eating Eidos pyramid image.
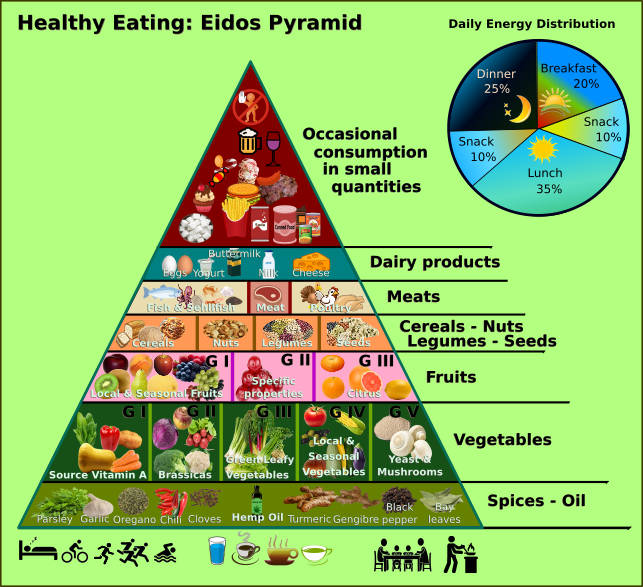
The Eidos food pyramid shows the importance of the food groups in the diet. The only way to guaranty a healthy life is including in the daily diet a wide variety of foods from the different groups, except from the unhealthy group that only should be ate occasionally in small quantities.
Also, it is important to have a daily regular pattern time for eating the meals. As well it is important to have a good rest, preparing and cooking foods, eating in a peaceful family environment and practice daily physical exercises.
A palatable selection of drinks such as different kind of teas can result in an increased fluid intake to maintain the adequate body hydration. Half an hour before physical exercise it is a good idea to drink at less a glass of water. All drinks should avoid added sugar.
Daily and weekly consumption
of recommended foods
Food group |
Food subgroup |
Foods |
Recommendations |
| Spices & Oil | Spices | Parsley, garlic, oregano, chili, turmeric, cloves, gengibre, sage, mustard, aprika, black pepper, bay leaves, etc. | Use multiple spices for seasoning and flavoring all meals. |
| Oil | Hemp seed oil | 10 ml (a tablespoon) per serving for dressing salads and other meals. | |
| Vegetables | Group I: Source of vitamin A | Carrots, spinach, yellow squash, red peppers, sweet potatoes. | At less 50-100 g per day. Include one or more of them in meals. |
| Group II: Brassicas | Rutabaga, turnip, cauliflower, broccoli, red cabbage, Chinese cabbage, radish, Brussels sprouts, kale, etc. | At less 50-100 g per day. Include one or more of them in meals. This group synthesise some secondaries metabolites with nutraceutical properties useful for preventing and reverting several kind of cancer. |
|
| Group III: Green leafy vegetables | Dandelion, lettuce, swiss chards, fennel, celery (leaves and roots), green onions, etc. | At less 50-100 g per day. Include one or more of them in meals. They are good sources of fiber, high quality of carbohidrate and fatty acids, and vitamins and minerals; and a variety of active phytochemical compounds. |
|
| Group IV: Local and seasonal vegetables | Tomatoes, olives, onions, mais, beets, eggplants, green squash, cuccumbers, etc. | At less 50-100 g per day. Include one or more of them in meals. They are good sources of fiber, high quality of carbohidrate and fatty acids, and vitamins and minerals; and a variety of active phytochemical compounds. |
|
| Group V: Yeast and mushrooms | Yeast: Saccharomyces cerviceae | ~10 g per day. 1 tablespoon per day. |
|
| Mushrooms | 30-50 g per day. | ||
| Fruits | Group I: Local and seasonal fruits | Apples, kiwi, pears, Plums, Peaches, Grapes, bleuberries strawbarries, bananas, avocados, papayas, etc. |
120 g fresh fruits/day. Eat one or more pieces of different fruits. |
| Group II: Cranberries | Cranberries fresh |
120 g fresh berries/day or, 100 ml pure juice/day. Useful for preventing urinary infections. |
|
| Group III: Citrus | Grapefruit Orange Tangerine, etc |
0-120 g per day. A rich source of flavonones and they have a wide range of physiological and pharmacological effects. |
|
| Lemon | At less 20 ml or 1/2 lemon dressing salads. | ||
| Cereals - Nuts - Legumes - Seeds | Cereals | Brown bread | ~70 g (2 slices) per day. |
| Brown rice | 60 g per day or several times per week. | ||
| Brown pasta | 60 g 1-2 times per week. | ||
| Other cereals | ~60 g per day of a variety of cereals. | ||
| Nuts | Walnuts Almonds Mixed nuts, etc. |
10-30 g per day. Good sources of nutrients. |
|
| Legumes | Beans, chickpeas, green peas, lentils, etc. | 30-50 g several times per week. | |
| Seeds | Hemp seeds | 10-30 g 3 o more times per week. Good source of proteins equivalent to eggs and soja beans. |
|
| Squash, moringa, sunflower, chia, flax, sesame, variety of seeds | 10-30 g several times per week. Good sources of nutrients. |
||
| Meats | Fish & shellfish | Salmon, sardines, tuna, trout, etc Clamps, scallops, oysters, shrimps, mussels, lobsters, etc. |
100 g no more twice or three times per week. |
| Red meats | Cow, pig, etc. | 80-100 g once per week. | |
| Poultries | Chicken, turkey, duck, etc. | 100 g at less 3 or 4 times per week. | |
| Dairy products | Dairy products | Buttermilk Greek yogurt Yogurt |
80-100 g per day. |
| Cheese | 25-50 g per day. | ||
| Low fat milk | 50-100 ml per day. | ||
| eggs | Once per week. | ||
| Unhealthy foods | Occasional consumption in small quantities | Sugar Soft drinks Processed meats Fried and fast foods Pastry and deserts Candies and snaks bars Canned foods Alcholic drinks |
Try to avoid as much as possible. Only eat them occasionaly and in very small quantities. |
| Drinks | Water - Infusions 1.5-3 liters per day |
Water | Each time needed. |
| Coffe | 240 ml no more three times per day. | ||
| Teas | 240 ml several times per day. |
EIDOS Drinks Pyramide
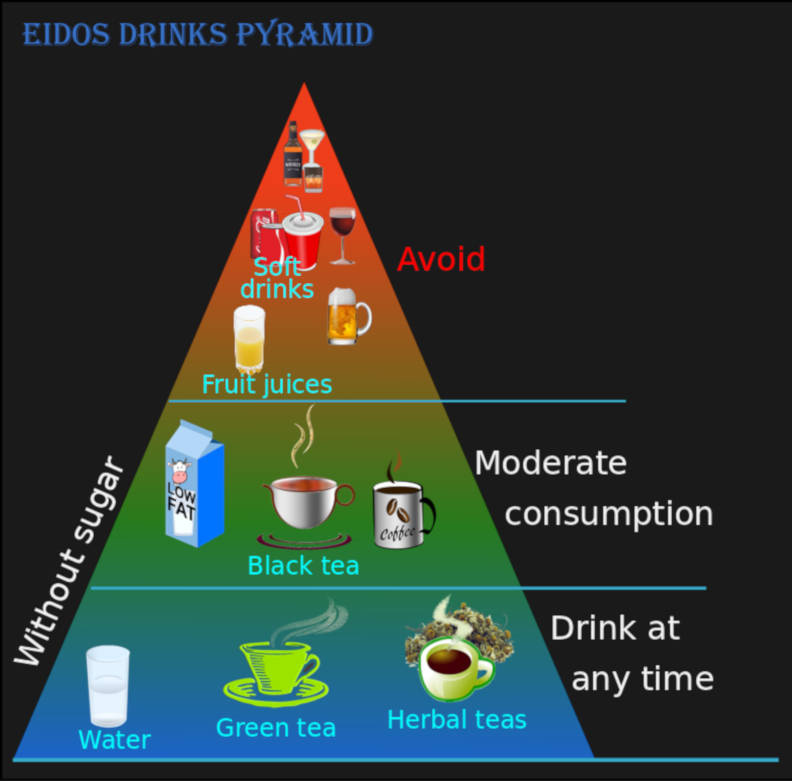
For satisfying the needs of the adequate requirement of water or fluid intake per day it is possible to drink a variety of fluids as substitute of water.
Despite water has the advantage of fulfilling hydration requirements without providing additional energy it is not the preferred drink chosen by people. It is important to choose good beverages as alternative to satisfy the adequate requirements of fluid per day.
The Eidos diet suggests to drink a variety of beverages as an alternative of water such as a combination of variety of teas, including coffee and low fat milk with moderation. Alternative beverages should be sugar-free. It is not recommended to drink juice fruits because despite they are extracted from fruits, pulp and fibre are removed and they have a high concentration of natural sugars such as fructose and sucrose. Fruit juices should not be consumed in no more than 200 ml per day; it is better eating the whole fruit. People should avoid drinking soft drinks and alcoholic drinks.
Tea is the second most commonly consumed beverage in the world after water, and black, oolong and green teas are all produced from the leaves of the plant Camellia sinensis using different processing methods, also there are a wide variety of herbal teas available, for example, chamomile, peppermint and fruit teas, which are often caffeine free[1].
All the studies on hydration found that tea status drinking had no adverse effects on hydration status, indicated by blood and urine markers remaining in the normal ranges and tea provided similar hydration benefits to water, as no statistical differences in blood and urine markers were reported when these conditions were compared[2].
The advantage of drinking teas and herbal teas is that they have phytochemicals with nutraceutical properties that can benefit the health.
___________
[1] Benelam , B. and Wyness, L. 2010. Hydration health: a review. British Nutrition Foundation Nutrition Bulletin, 35, 3–25.
[2]Ruxton, Carrie. 2016. Tea: hydration and other health benefits. CPD, volume 26 number 8.
eidos-project.net © 2016- 2024